|
P2P
|
Client-Server
|
|
No central server
|
Central Server
|
|
Suitable for small
business org.
|
Scalable
|
|
Inexpensive
|
Expensive
|
|
Not secure
|
Secure
|
Saturday, July 16, 2016
P2P Systems Techniques and Challenges
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 5:03 AM with No comments
Peer-to-peer (P2P) applications have recently attracted a
large number of Internet users. Traditional P2P systems however, suffer from
inefficiency due to lack of information from the underlay, i.e. the physical
network.
Despite all the efforts been put in, a gap has been
witnessed between the simulation figured and results and actual real world
scenarios. Some researchers have admitted that these simulation results can no
way be compared to what they might face in real world networking environment,
other than a few researches.
Notable effort and resources are yet to be put into most
of these researches in order to make them viable for a real world practical
application. One such example is the peer to peer communication optimization
which can be very useful for multiplayer gaming and overall file sharing and
communication on the Internet.
Other such experiments in the labs have shown extremely
positive results which can change the dynamics of underlying networks
New P2P Systems:
• File sharing was first P2P application
• Other applications are coming to light
• BitTorrent: focus more on content
distribution than file sharing
– Makes use of common research
result (DHT) since 2005
• P2P extending beyond file sharing: Skype
– Skype is a P2P telephone
“system”
– Can call other computers, or
normal phones
– Based on the KaZaA network
• P2P streaming systems
– PPLive, PPStream
Conclusion:
Both the peer to peer and
client server architectures have their own pros and cons. It depends on the
organizational architecture that what suits the best in a particular scenario.
Client Server
architectures are expensive and can accommodate large number of users. They are
scalable.
For an organization with
30 nodes and data security not an issue, peer to peer is the recommended
network architecture. It is cost effective as well as suitable for small
organizations.
P2P Overlay Architecture
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 5:00 AM with No comments
P2P overlay
network has a wide spectrum of communication frameworks in which peers build a
self-organized system that is fully distributed and cooperative. Figure 1
depicts the abstract P2P overlay architecture showing different components of
the overlay.
The Network
Communication layer describes the network characteristics of an end system/node
connected via internet, small wireless or sensor-based devices.
The Overlay
Nodes Management layer plays its part as management of peers which includes
discovery of peers and optimized routing algorithm.
The Features
Management layer deals with security, reliability, fault tolerance, and
robustness of P2P system.
The Service
Specific layer is to provide support to Application layer to utilize the
underlying resources in an efficient manner. It schedules the parallel and
computation-intensive tasks, and performs task like file management and
provides content. Here meta-data describes the information about content stored
across the peers and their location information.
The Application level layer describes the actual
functionality implemented over the underlying P2P overlay networks.
Structured
P2P:
In structured overlay network the network assigns keys to
data items and organizes its peers into a graph that maps each data key to a
peer. Such structured P2P systems use the Distributed Hash Tables as a
substructure where data objects either values or location information is
placed.
Unstructured
P2P:
In unstructured overlay networks the overlay network
organize peers in a random graph in flat or hierarchical manner and uses
flooding or random traversing or expanding Time-To-Live search on the graph to
query content stored on overlay networks.
Distributed
Hash Tables:
Current widely-used P2P networks rely on central
directory servers or massive message flooding, clearly not scalable solutions.
Distributed Hash Tables (DHT) are expected to eliminate flooding and central
servers, but can require many long-haul message deliveries.
Although many theoretical schemes for minimizing routing
information have been proposed and many designs for DHTs have recently become
prominent discussion topics, we are unaware of any practical and efficient
system combining both.
Latest
Research in P2P:
In order to get the latest that is happening in this area
I decided to get some latest research papers online and went through them.
According to my limited research that I did on this topic I found out that the
over lay under lay mapping is very important in this domain of network models. The
nodes that are that are connected logically should be close to each other
physically as well in order to avoid network congestions and other delays.
Following is a brief summary of the latest research being
carried out.
EGOIST Overlay Routing
using Selfish Neighbor Selection
This paper discusses the
issue of connectivity management, folding new arrivals into an existing
overlay. Work has been done on this matter before dealing with devising
practical heuristics for specific applications designed to work well in real
deployments, and providing abstractions for the underlying problem that are
analytically tractable, especially via game-theoretic analysis. The authors of
this paper have combined these two approaches and came up with a distributed
overlay routing system called “Egoist”. Connectivity management is called upon
when having to wire a newcomer into the existing mesh of nodes (bootstrapping),
or when having to rewire the links be- tween overlay nodes to deal with churn
and changing network conditions. Connectivity management is particularly
challenging for overlay networks because over- lays often consist of nodes that
are distributed across multiple administrative domains, in which auditing or
enforcing global behavior can be difficult or impossible.
In a typical overlay network, a node must
select a fixed number (k) of immediate overlay neighbors for routing traffic or
queries for files. To solve this, the authors tried and tested the selfish
neighbor selection technique which was different from traditional techniques.
DHTs are able to provide the best possible indexing of objects in a network. On
the other hand, routing of traffic on DHTs has been shown to be sub-optimal due
to local forwarding [17, 24]. Egoist can be integrated as a different layer in
DHTs; when an object is mapped onto a node, Egoist is responsible to optimally
route the content. In Egoist, a newcomer overlay node vi connects to the system
by querying a bootstrap node, from which it receives a list of potential
overlay neighbors. The new- comer connects to at least one of these nodes,
enabling it to participate in the link-state routing protocol running at the
overlay layer. As a result, after some time, vi obtains the full residual graph
G−i of the overlay. By running all-pairs shortest path algorithm on G−i, using
Dijkstra’s algorithm, the newcomer is able to obtain the pair-wise distance
(delay) function dG−i . In addition to this information, the newcomer estimates
dij , the weight of a potential direct overlay link from it- self to node vj ,
for all vj ∈ V−i. Using the values of dij and dG−i , the newcomer connects to
G−i using one of a number of wiring policies. Each node listens to all the
control messages of the link state protocol and propagates them only to its
immediate neighbors. In order to reduce system’s control traffic, each node
propagates only unique messages by dropping messages that have been received
more than once or have been superseded. In Egoist, a node selects its neighbor
based on best response strategy. They also employed fast approximation versions
based on local search instead of long arithmetic computation which will not
only reduce computational cost but also enhance scalability. Egoist’s BR
neighbor
selection
strategy assumes that existing nodes never leave the overlay. Therefore, even
in an extreme case in which some nodes are reachable through only a unique
path, a node can count on this path always being in place. This can be a one
set back of this technique. Egoist also deals with the cheating nodes (using
the system to route one’s own traffic but denying routing to any incoming
traffic from other nodes) very efficiently in which the nodes periodically
select a random subset of remote nodes and “audit them” by querying the
coordinate system for the delays of the outgoing links of the audited nodes and
comparing them to the actual values that the audited nodes declare on the
link-state routing protocol.
Delays are
natural cost metrics for many applications, especially those involving
interactive communication. To obtain the delay cost metric, a node needs to
obtain estimates for its own delay to potential neighbors, and for the delay
between pairs of overlay nodes already in the network. Using ping, one-way
delay is estimated to be one half of the measured ping round-trip-times (RTT)
averaged over enough samples. The performance of the system was measured on the
basis of different cost metrics such as link and path delays, node load and
available bandwidth. Results of the experiments are represented graphically
which showed a positive outcome and the system out performed similar previous
work done relating to this. They’ve also made it available for use for any
third party application through their API. This way, both the application and
its Egoist node run at the same node.
This was a very comprehensive paper about the work that
authors of this paper carried out. All the basic working, idea behind it and
the results were shown in detail explaining every aspect if the new system that
they’ve designed. This work definitely have a lot of real world application as
the one they’ve explained (Multiplayer P2P gaming) which makes it an extremely
appealing and the best strong point of this paper.
Other Hot Areas:
·
Improving Unstructured Peer-to-Peer Systems by Adaptive Connection
Establishment
· Improving
the Interaction between Overlay Routing and Traffic Engineering
·
ISP-Friendly
Live P2P Streaming
·
Scalable
Resilient Overlay Networks Using Destination-Guided Detouring
Peer to peer
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 4:23 AM with No comments
Peer to peer is a network model in which all the nodes
(peers) interact with each other directly. There is no central server involved
to handle the requests.
P2P is in contrast to Client-server in which there are
clearly defined roles for client and server.
An
example of p2p organization of nodes
Nodes can be organized in any topology but the real
essence od peer to peer systems is that there is no central service provider
involved but peers interact with each other on equality basis. It has its pros
and cons.
Introduction:
Peer to peer systems are those systems which take
advantage of storage, cycles, human presence or content available at the end
systems of the internet while overlay networks are termed as those networks
that are constructed on top of other networks e.g. IP. So peer-to-peer overlay
network is a network which is created by the internet peers in the application
layer on top of the IP network. In these types of systems the end nodes/systems
share their resources such as processing power, network bandwidth and memory
storage among themselves to accomplish a set of common tasks in a distributive
manner without need of any central coordination system. These systems are
self-organized. All peers organize themselves into an application layer on top
of IP layer. These are highly scalable and have the capability to grow
accordingly with utilization. End systems empowers each other as the consumers
are also provider of their resources at the same time. P2P overlay networks are
highly reliable too as there is no single point of failure and redundant
overlay links ensures availability if a single link got damage or disconnected.
These systems are easy to deploy because they are self-organized and there is
no need to deploy any server. Now a days peer to peer networks are being used
in many ways. Some of them are P2P file sharing applications like Napster,
Gnutella, Kaza, Emule, Edonkey, Bittorent etc., media streaming, Grid
computing, community networks, instant messaging systems, online chat networks
and a very interesting use is Bitcoin a peer-to-peer based digital currency. In
peer-to-peer overlay systems there is symmetry in roles where every nodes is
client and a server at the same time.
P2P
Basic Principle:
The main concept of the p2p and its characteristics are;
–
Self-organizing, no central management
–
Resource sharing, e.g., files
– Based
on voluntary collaboration
– Peers
in P2P are all equal (more or less)
– Large number of peers in the network
Definition of P2P:
A P2P system exhibits the following
characteristics:
1. High
degree of autonomy from central servers
2.
Exploits resources at the edge of the network
3.
Individual nodes have intermittent connectivity
• No strict requirements, instead typical characteristics
Virtualization
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 4:15 AM with 1 comment
Virtualization:
It refers to the concept
of creating something that does not exist in real. In virtualization an
imaginary version of something is created rather than creating that in real.
The concept of
virtualization is not limited to software only. Hardware resources are also
associated with this concept now.
Definition:
“It is a
technique for hiding the physical characteristics of computing resources from
the way in which other systems, applications, or end users interact with those
resources”
History:
It was started in the
60’s by IBM M44/44X
It was abandoned in the
80’s and 90’s because the cheaper x86
machines were more famous.
But VMware started
virtualization in 99.
CPU Virtualization
Architecture:
Full Virtualization:
Virtualization layer
uses binary translation to replace with privileged instruction with
instructions that have the same affect on the Virtual Machine.
Para Virtualization:
Guest operating systems
is modified to call functions instead of issuing privileged instructions.
Hardware assist:
CPU support of
virtualization is present that eliminates the needs for binary translation.
Memory Virtualization Architecture:
Hardware supports
virtual to physical translation of messages. Another layer from guest physical
to host physical is needed for virtualization. This is done with shadow page
tables that hold guest virtual to host virtual translation that are loaded to
the hardware for direct translation.
Client Server Architecture
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 4:09 AM with No comments
The client server is one of the most common and widely
used models in the world right now. In this model there is a dedicated machine
called server that has all the resources (software and in some cases hardware
too) and other terminal make use of those resources by sending request to that
central server.
It is a distributed application structure in which the
server serves the clients as per their requests. There are many models
developed and design for the handling of these requests from the client. Mostly
FIFO is implemented in which the clients coming first are served first.
Servers
are powerful machines normally that are dedicated to manage the resources like
disk drives, printers etc.
The
main advantage of client server architecture is the security that it provides.
The content is placed on one central server so you just have to secure that
machine. The point that comes against this argument is the single point of
failure aspect of client server model that has been continuously under debate
for a very long time now.
Definition of Client-Server Network model:
“An architecture in which the user's PC (the
client) is the requesting machine and the server is the supplying machine, both
of which are connected via a local area network (LAN) or a wide area network
(WAN) such as the Internet”
Advantages of Client-Server Network model:
Centralization:
The main advantage of
the Client Server architecture is the centralization of resources. There is
just one place that needs that needs ot be managed in terms if data security
and access rights.
Scalability:
These systems are
scalable and any number of clients can be handled if the server capacity is
increased. The main reason behind that is that any element can be upgraded as
and when wanted so it increases the computing power of the server.
Flexibility:
The modularity in the system architecture
provides the benefit of flexibility. Any change can be reversed or deployed as
per requirements. The system is adaptable to these changes as it has been
designed that way.
Interoperability:
All the components involved
in this architecture work together. These components include client, server and
other network components.
Security:
It is easy to maintain a
single node’s security then to manage a distributed system in which nodes come
and leave any time.
Disadvantages of Client-Server Network model:
Overloaded Servers:
Traffic congestion is
caused when the servers are busy for longer periods of time. The client
requests start queuing up which can cause the network to slow down.
Single point of Attack:
Due to the centralized
server, the network can be attacked by exploiting a single machine only. The
security of the server become ultra important when there is just one point of
attack.
Single point of failure:
Whole of the network can
go down if there is just one point that is serving the nodes. The super node
(server) has all the information related to the network .If that node is
compromised then it will be impossible to communicate through that network as
nodes don’t have information of the network independently.
Tuesday, July 12, 2016
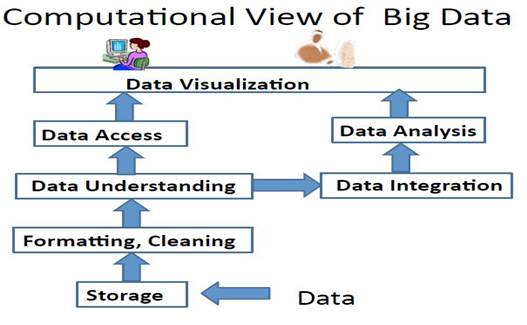
What is big data?
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 11:41 PM with No comments
Ans:
The data lying in the servers of your company was just data until
yesterday – sorted and filed. Suddenly, the slang Big Data got popular and now
the data in your company is Big Data. The term covers each and every piece of
data your organization has stored till now. It includes data stored in clouds
and even the URLs that you bookmarked. Your company might not have digitized
all the data. You may not have structured all the data already. But then, all
the digital, papers, structured and non-structured data with your company is
now Big Data.
Big Data is essentially the data that you analyze for results that
you can use for predictions and for other uses. When using the term Big Data,
suddenly your company or organization is working with top level Information
technology to deduce different types of results using the same data that you
stored intentionally or unintentionally over years.
Big Data Concepts:
This is another point where most
people don’t agree. Some experts say that the Big Data Concepts are three Vs:
1. Volume
2. Velocity
3. Variety
Some others add few more Vs to the concept:
4. Visualization
5. Veracity
(Reliability)
6. Variability
and
7.
Value
ü "Big
Data Are high-volume, high-velocity and/or high-variety information assets that
require new forms of processing to enable enhanced decision making, insight
discovery and process optimization”.
ü Complicated
(intelligent) analysis of data may make a small data “appear” to be “big”
ü Bottom
line: Any Data that exceeds our current capability of processing can be
regarded as “big”
What is Cloud Computing?
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 11:33 PM with 1 comment
Ans:
"Cloud
computing is a new approach that reduces IT complexity by leveraging the
efficient pooling of on-demand, self-managed virtual infrastructure, consumed
as a service"
A
film spotlighting the aspects of using cloud storage that should be addressed
by users for data and personal security. Cloud Computing is the
internet-based storage for files, applications, and infrastructure. One could
say cloud computing has been around for many years, but now a company may buy
or rent space for their daily operations. The cost savings in implementing a
cloud system is substantial, and the pricing for use of cloud computing can
easily be scaled up or down as determined by necessity.
According to Wikipedia:
“Cloud
computing is Internet-based computing, whereby shared resource, software, and
information are provided to computers and other devices on demand, like the
electricity grid.”
Generally speaking, cloud computing can
be thought of as anything that involves delivering hosted services over the
Internet. According to NIST Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous,
convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing
resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that
can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or
service provider interaction.
What is 5G? What are the Security Concerns?
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 11:27 PM with No comments
Ans:
5G
is going to become necessity for the future of the world due to the increasing
traffic rate of the data, voice or video streaming in this modern era. The
present technologies such as 3G and 4G cannot fulfill the future requirements
of the increasing capacity of the traffic of internet data. There is no unique
definition for 5G. It is basic step to know that “What is 5G?” in real sense.
First of all, we have to take step to clarify the real means of 5G in
technological sense.
According
to researchers, Scientists and Engineers the 5G will facilitate user with 1000
times greater bandwidth as well as 100 times larger data rate to cover the huge
applications of future mobile stations. [2] It is also expected that various
techniques to fulfill the user requirements which will be used in 5G, one of
them will be THz band mobile communication. [3] The 5th wireless mobile internet networks are real
wireless world which shall be supported by LAS-CDMA, OFDM, MC-CDMA, UWB,
Network-LMDS and IPv6. Both 4G and 5G has basic protocol which is IPv6.
A number of generation changes have been
experienced by mobile technologies,
which
have transformed the cellular background into a global set of interrelated
networks. By the 2020, fifth generation will supports the voice, video
streaming and very complex range of communication services over more than Nine
billion of the subscribers as well as the billions of devices which will be connected to each
other. But what is 5G? 5G provides
the new path to think.
It
includes radical network design for installing machine-type communication
(MTC). And 5G networks will be able to provide efficient support applications
with widely varying operational parameters, providing greater elasticity to
install services. As the previous generations, 5G is combination of progressed
network technologies.
Coming technology (5G) would have the ability
to share date everywhere, every time by everyone and everything for the benefit
of human, businesses and society as well as the technological environment by
using bandwidth of unlimited access for carrying information. The year 2016 is
an expected year to take steps for proper and Standard activities are started
and leading to commercial availability of the equipment and machinery around
2020. Future technology (5G) is much more than new
set of technologies that will require enormous equipment/devices or machinery
upgrades as compare to the previous generations. The purpose of this technology
is to build on the development that the telecommunication systems have already
been reached. The complementary technologies (Combination of core and cloud
technologies are called complementary technologies) which evolve many existing
radio access will be used to cater more traffic of data, more types of devices
under different operating requirements with different cases in 5G.
Nevertheless, a universal
agreement is building around the idea that 5G is simply integration of number
of techniques, scenarios and use cases rather than the origination of a new
single radio access technology. The estimated performance levels that 5G [6]
technologies will need to cater for:
§ 10 to 100 times higher typical user data rate,
§ 10 times longer battery life for low power devices,
§ 10 to 100 times higher number of connected devices,
§ 5 times reduced end-to-end latency,
§ 1000 times higher mobile data volume per area.
Figure
1 shows estimated performance levels of fifth generation technology need to
meet requirements.
Now the problem is that “How will we get
there?”
Next generation (5G) will mostly allow for connectivity. But this technology is
not developed in separation. The developing next generation will play
significant role in shaping various factors such as long term sustainability,
cost, and security and need to give connectivity to the billions of
subscribers. While the comprehensive conditions for 5G have nevertheless to be
set, it is clear that flexibility to accommodate for thousands of use cases is
the key to 5G and what it will enable. The parameters that 5G technology will
be developed upon include:
§
Data integrity,
§
Latency,
§
Smart communication.
§
Traffic capacity,
§
Data throughput,
§
Energy consumption,
§
Technology convergence.
A cognitive radio is an
intelligent radio that can be programmed and configured dynamically. Its
transceiver is designed to use the best wireless channels in its vicinity. Such
a radio automatically detects available channels in wireless spectrum, then
accordingly changes its transmission or reception parameters to allow more
concurrent wireless communications in a given spectrum band at one location.
This process is a form of dynamic spectrum management.
A we all know, one of the
fundamental issue is the increasing challenge of acquiring adequate spectral
resources in radio frequency bands to operate 5G cellular systems. All over the
world, a large amount of spectral resources are still utilized in a static and
therefore, inefficient manner. Hence, Cognitive Radio (CR), with the capability
to be aware of radio environments and flexibility adjust its transceiver
parameters, has drawn much attention in academia and recently also in industry
and has been proposed as an enabling technique to dynamically access the
underutilized spectral resources. The previous research on CR was focusing on
improving the utilization of radio spectrum resources mainly within the primary-secondary
user models in the UHF TV band. In 5G wireless communications, to meet the
challenging requirements of huge capacity, massive connectivity, high
reliability and low latency, CR is expected to play an important role in two aspects.
First, since the spectrum band for 5G will be extended to even mm Wave range,
CR can still be used to improve the spectrum utilization while protecting much
larger range of coexisting users and within broader types of spectrum sharing
models, such as licensed spectrum sharing (LSA) and dynamic spectrum leasing
etc. Second, 5G will take aggressive spatial reuse of spectrum as one of the
key enablers with new techniques such as massive MIMO and Ultra-dense
Deployment. In this context, CR can be used to mitigate the interference issues
from space, frequency and time domains with a very dynamic manner. We define an
attack on cognitive networks as any activity that results in
1.
Unacceptable interference
to the licensed primary users or
2.
Missed opportunities for
secondary users
Attacks against CRs and
CRNs are:
1.
Incumbent Emulation
attacks
2.
Spectrum Sensing Data
Falsification attacks
3.
Cross layer attacks
Security Concerns in 5G:
Where
there is information, there is a critical need for security. Security is one of
the important issues for the proposed adaptive and reconfigurable wireless
network testbed. The meaning of security is twofold. First, the data sent out
by the nodes should be encrypted, to prevent unauthorized users from
intercepting the data over the air. However, cryptographic algorithms impose
tremendous processing power demands that can be a bottleneck in high-speed
networks. The use of FPGAs for cryptographic applications has become highly
attractive.
Cryptographic
algorithms will be implemented on the two FPGAs on the proposed motherboard for
the nodes of the network testbed. However, for the network testbed for smart
grid, the optimal choice for the cryptographic scheme is the topic of ongoing
research. Second, the reconfigurable FPGAs in the network testbed should have
the capability of protecting themselves from being invaded or tampered.
Security
is more important than any other performance of interest for the micro grid. To
realize a secure system, security should pervade every aspect of the system
design, and be integrated into every system component. For information flow,
information security for the micro grid should include data confidentiality,
data authenticity, data integrity, data freshness, data privacy, public key
infrastructure, trusted computing, attack detection, attack survivability, intelligent
monitoring, cybersecurity, and so on. For power flow, autonomous recovery is
the main security consideration. The micro grid should have the capability of
performing real-time monitoring and quick response.
ü Heterogeneity
of wireless networks complicate the security issues. Dynamic reconfigurable,
adaptive and lightweight security mechanism should be developed.
ü Authentication
of user is a big problem in heterogeneous wireless networks.
ü Security
in smart grids may be generalized into two main areas:
·
Physical layer
·
Cybersecurity
ü Interoperability
of Security enabled IoT.
ü Security
for M2M Communication.
Saturday, August 15, 2015
What is Website designing?
Posted by Sarfraz Haider on 7:36 AM with No comments
Website
designing is very large platform in this world. Every person want to start
own
business at home. But this is true it is not easy job. Every person wants to
earn money from internet through the website. Website is main source to earn
money from internet. Google adsence is a big way to earn money from internet.
When we design and develop a complete site then we customize in google through
google webmaster tool. We add the web pages in Google Master tool then Google
index the our all web pages.
Website Designing:
When
we start a build the website then we must think about in this thing which data
we provide to common user. These are languages must use in website designing.
1. HTML
2. CSS
3. CSS3
4. HTML5
HTML:
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup
Language. HTML is basic language of Website designing. We cannot develop and
design the website without HTML. HTML provides us basic tags and elements for
build the website.
CSS:
CSS
stands for Cascading Style
Sheets. We can use the colors, width, height, padding, margin, borders,
color adjustment, hover, text-style, and more properties for designing the
website.
CSS3:
CSS3
is most advance language. We can design stylish text box, stylish popup menus,
text shadow, text rotate, and more advance properties in website.
HTML5
HTML5
is most advance Language. We can add the movies, audio files, video files and
other files with the help of HTML5. We can also make mobile application, web
games, web base application in HTML5.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)