 |
| Network |
The
ability to expend beyond the limit of a single computer in a single office has
expended the reach of the PC to global proportions. Two technologies have
driven this expansion: computer networking and the portable computer. In this
topic, we first take a look at how the networks that link up computers on a
global scale are put together. Then we examine the portable computer, whose
introduction has allowed users instantaneous access to the computing and
networking power of all the latest computer technology anywhere they go.
A
network is defined as two or more computer linked together for the purpose of
communicating and sharing information and other resources.
Basic
Requirements Of a Network
In order for a network to function,
three basic requirements must be met. It must provide connections,
communications and services.
Connections
Connections include the hardware
(physical components) required to hook up a computer to the network. Two terms
are important to network connections.
The
network medium:
The network
hardware that physically connects one computer to another. This the cable
between the computers.
The
network interface:
The hardware
that attaches a computer to the network medium and acts as an interpreter
between the computer and the network. Attaching a computer to a network
requires an add in board known as a network interface card (NIC)
Communications
Communications establish the rules
concerning how computers talk and understand each order. Because computers
often run different software, in order to communicate with each other they must
speak a “shared Language” Without communications, computers cannot exchange
information and remain isolated.
Services
A service defines those things a
computer shares with the rest of the network. For example, a computer can share
a printer or specific directories or files. Unless computers on the network are
capable of sharing resources, they remain isolated, even though physically
connected.
Networking
Next we look at how the basic
elements of connections, communications, and services work together to make
networks function property
·
The
connections must operate so that any computer can send to receive electrical
signals (data) across the physical media that link them
· Communications
must function so that when one computer sends a message, the receiving computer
can listen and understand the message.
· Computers
on a network must either provide a services to other computers or make use of a
service provide be other computers.
Local
Area Networks
A
LAN (Local Area Network) is a network that covers a limited distance (usually a
single site of facility) and allows sharing of information and resources. A LAN
can be as simple as two connected computers, or as complicated as a large site.
This type of network is very popular because it allows individual computers to
provide processing power and utilize their own memory, while programs and data
can be stored on any computer in the network. Some of the older LANs also
include configurations that rely totally on the power of a mini or mainframe
computer (a server) to do the entire network. In this case the workstations are
no more than “dumb” terminals (a keyboard and a monitor)
Wide
Area Networks
A wide area network (WAN) spans
relatively large geographical areas. Connections for these sites require the
use of ordinary telephone lines, T1 lines, ISDN (Integrated Services Digital
Network) lines, radio waves or satellite. WANs can be accessed though dail-up connections
using a modem or leased line direct connection. The leased-line method is more
expensive but can be cost effective for transmission of large volumes of data.
Types
of Networks
There are essentially two types of
networks. They differ in how information is stored how security is handled, and
how the computers on the network interact. In a peer to peer network, each
computer acts as either a server (sharing its data or services with other
computers), or a client (using data or services on another computer depending
on the user’s needs. Each user, or workstation, established its own security
and determines which resources are available to other users. Typically these
networks are limited in size (15 to 20 workstation). MS Windows for workgroups,
Windows 95, and windows 98, Windows NT workstation, Windows 2000, Novell
NetWare, UNIX are Linux are some software packages available for peer-to-peer
networking.
Network
Topology
LAN design is called topology.
Topology describes he appearance or layout of a network and how data flows
through the network. There are three basic types of topologies, Star , bus,
Ring.
Star
Topology
In a star network, all devices are
connected to a central point called a hub. These hubs collect and distribute
the flow of data within the network. Signals from the sending computer go to
hub and are then transmitted to all computers on the network. Large networks
can feature several hubs. A star network is easy to troubleshoot because all
information goes through the hub, making it easier to isolate problems.
Bus
Topology
In a bus network, all devices are connected to
a single linear cable called a trunk (also known as a backbone or segment).
Both ends of the cable must be terminated (like a SCSI bus) to stop the signal
from bouncing. Because a bus network does not have a central point, it is more
difficult to troubleshoot than a star network. A break or problem at any point
along bus can cause the entire network to go down.
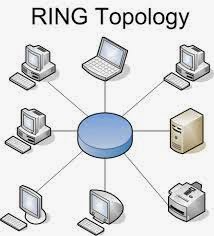
Ring
Topology
In ring topology the first computer
connected with second computer. The second computer connected to with third
computer similarly the last computer connected with first computer. This loop
of computer is also called ring topology. In ring topology optic fiber is used.
Network Cabling
All networks need cables. The three
main type are twisted pair cable (TP), coaxial cable, and fiber optic cable
(FDDI-Fiber Distributed Data interface).
Twisted
Pair Cable
Of the two types, UTP is the most
common. UTP cables can be further divided into six categories.
Ø Traditional telephone cable. Carries voice but not data.
Ø Certified UTP for data transmission of up to 4 Mbps (megabits per
seconds). It has four twisted pairs.
Ø Certified UTP for data transmission of up to 10 Mbps. It has four
twisted pairs
Ø Certified UTP for data transmission up to 16 Mbps. It has four
twisted pairs.
Ø Certified UTP for data transmission up to 100 Mbps. It has four
twisted pairs.
Ø Certified UTP for data transmission up to 1000 Mbps. (Gigabit
Ethernet) It has four twisted pairs.
CAT
5 Cabling Issues
Distance Limitations
Ethernet networks use
unshielded twisted pair (UTP) category 5 cables. CAT 5 cable runs should not
exceed 100 meters.
CAT
6 Cabling Issues
Distance Limitations
CAT 6 used to carry Ethernet
10base-T, 100Base-T, and 1000Base-T (Gigabit Ethernet) connections. Cat 6 cable
is backed with more stringent specifications for crosstalk and system noise
than earlier cabling standards.
Connectors
There are two different types of RJ
45 connectors. There is the “bent tyne” connector intended for use with solid
core CAT5, and then there is the “aligned tyne” connector for use with stranded
CAT5 cable.
Wiring/Color Coding for CAT5 and CAT6 Cable
CAT5
cables are typically terminated with RJ-45 connectors. Two types of RJ-45
connectors.
Two wires
color-code standard apply: EIA/TIA 568A and EIA/TIA 568B. The codes are
commonly dedicated with RJ-45 jacks as follows (the view is from the front of
the jacks).
Coaxial
Cable
Coaxial
cable is found in two types thin (Thin Net) and thick (Thick Net). Of the two
Thin Net is the easiest to use. It is about one quarter of an inch in diameter,
making it flexible and easy to work with (it is similar to the material
commonly used for cable TV). Thin Net can carry a signal about 605 feet (185
meters) before the signal strength begins to suffer. Thick Net on the other
hand is about three eigths of an inch in diameter. This makes it a better
conductor it can cary a signal about 1640 feet (500 meters) before signal
strength begins to suffer.
Fiber
Optic Cable
Fiber Optic cable is made of light
conducting or plastic fibers. It can carry data signals in the form of
modulated pulses of light. The plastic core cable are easier to install, but do
not carry signals as far as glass core cables. Multiple fiber cores can be
bundled in the center of the protective tubing.
 |
| Fiber Optic Cable |
When both material and installation
costs are taken into account, fiber optic cable can prove to be no more
expensive than twisted pair or coaxial cable. Fiber has some advantage a
reliable and secure transmission media. It also supports very high bandwidths
(the amount of information the cable can carry), so it can handle thousands of
times more data than twisted pair or coaxial cable.
Cable
lengths can run from .25 to 2.0 kilometers depending on the fiber optic cable
and network. If you need to network multiple buildings, this should be the
cable of choice. Fiber optic cable systems require the use of fiber compatible
NICs.















0 comments:
Post a Comment